Oxidative Stress after a Brain Injury
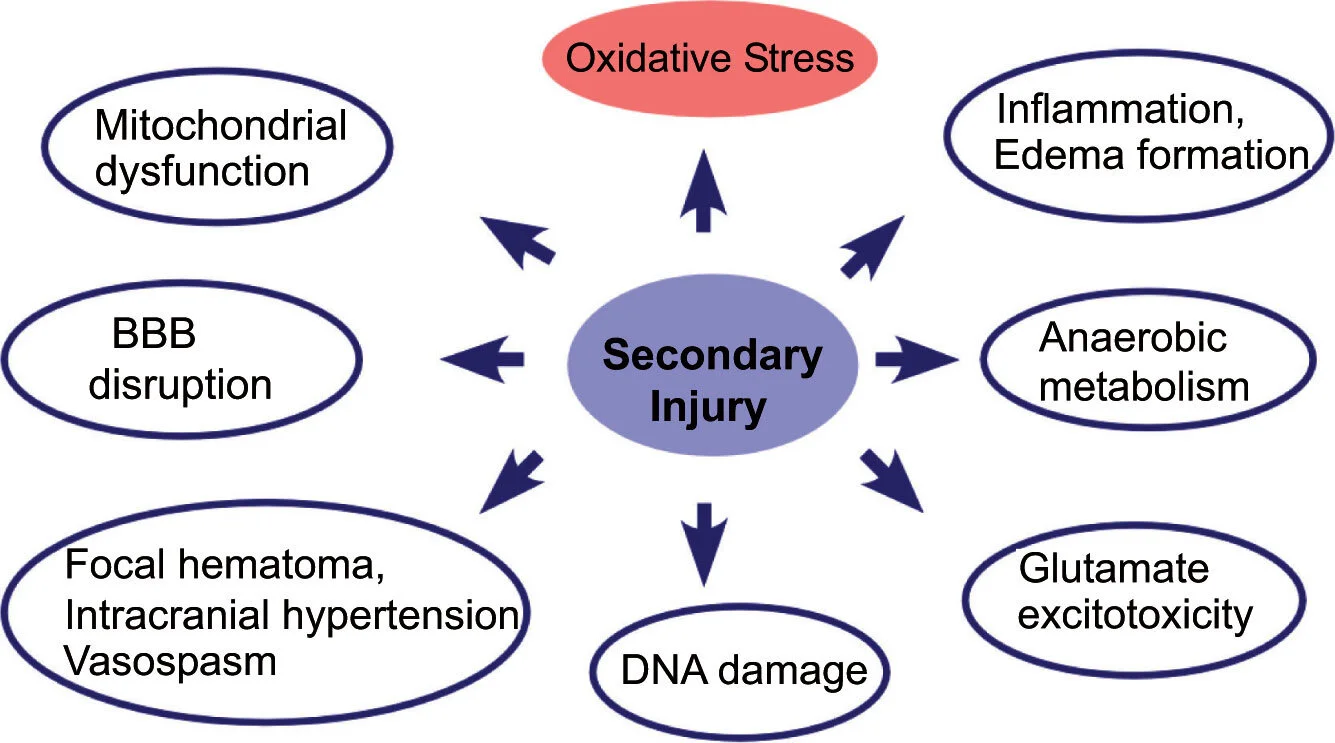
The Neurometabolic Cascade begins with an initial or primary injury, often a hit to the head, causing a traumatic brain injury. If not treated, the neurometabolic cascade sets in motion secondary complications that often linger for years, even decades. So seeking medical treatment following even mild brain injury events is so important. Reducing the possibility of long-term symptoms requires stopping secondary influx, including Oxidative Stress.
Oxidative stress occurs along with blood barrier disruption, inflammation, excitotoxicity, cell death, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Imbalances between multiple biochemical processes cause it within the brain. This process leads to imbalances between products of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the removal of ROS. This overproduction is most often due to too much glutamate or excitotoxicity and depletion of glutathione, the main antioxidant.
What is important to remember in seeking treatment: that oxidative stress will lead to further mitochondrial dysfunction, lipid peroxidation, oxidation of proteins, and DNA/Cell death.
Oxidative stress is basically ‘the straw that breaks the camel’s back’ in TBI recovery.
Oxidative stress can lead to Immunotoxicity where the body’s immune system attacks the injured brain. The theory is that glutamate levels rise and activate immune receptors related to oxidative stress.
What can we do to decrease the effects of Oxidative Stress?...
Increase Antioxidants of course!
Eat Polyphenol foods like blueberries
Eat Bioflavonoids rich foods
Take NAC- a precursor to glutathione
Take Glutathione
Take Melatonin
Take Resveratrol (check-in on Friday’s post to learn more about this vital supplement)
PMID: 29952272, 29207487, 25232881